The transition toward decarbonization, coupled with the rise of Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) and Renewable Energy Sources (RES), is transforming how electricity distribution systems operate. In this context, Local Flexibility Markets (LFMs) have emerged as a key mechanism to enhance grid reliability [1]. HEDNO, the Greek Distribution System Operator, is actively exploring the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into grid operations, focusing on forecasting energy demand at the secondary substation level to support effective participation in LFMs.
Explicit flexibility, defined as the proactive response of energy consumers to DSO-initiated signals, is fundamental to the success of LFMs [2]. However, its utilization depends heavily on the accurate forecasting of energy consumption and the proper design of baseline methodologies [3]. HEDNO’s approach involves forecasting energy demand using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neural networks, applied to telemetered data from secondary substations. These substations serve as aggregation points for residential consumers, offering a more stable forecasting base than individual household loads [4].
To improve accuracy, the forecasting model incorporates external variables such as temperature and cloud cover, retrieved from Open Meteo. The enriched dataset is processed into train and test sequences and evaluated using the Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) metric. A MAPE of 0.085 was achieved for the 6th Market Time Unit (MTU), making the forecasts suitable for intraday market applications.
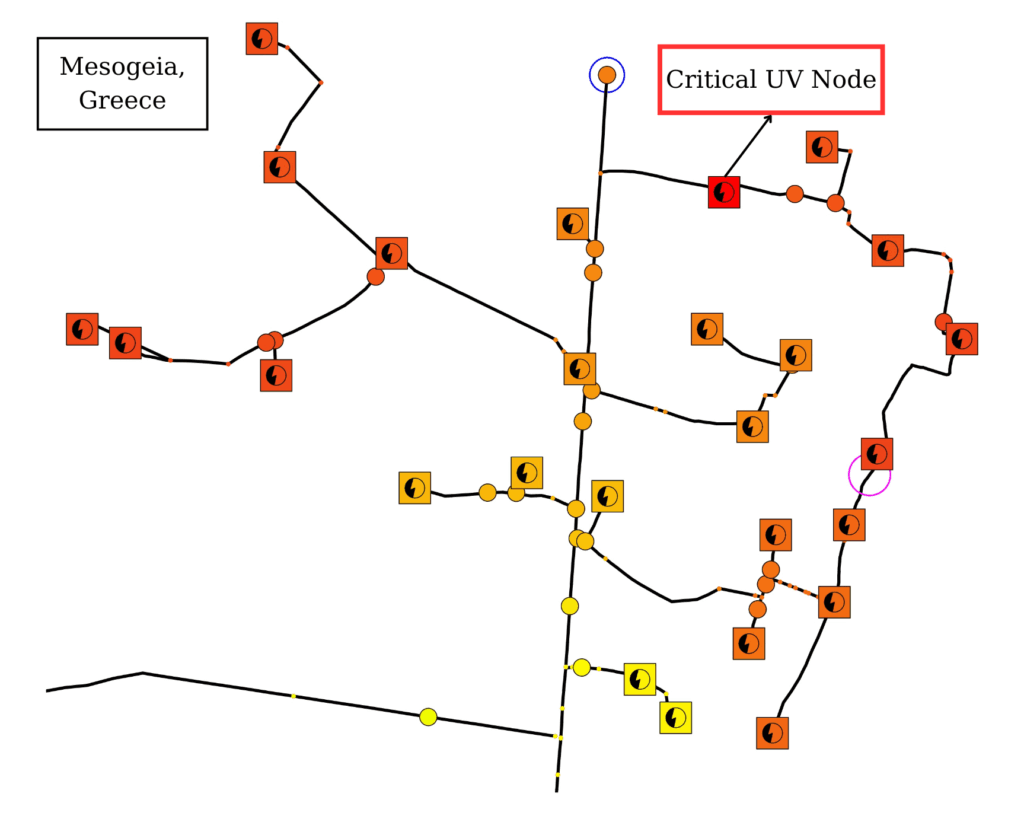
These forecasts are integrated into grid simulations using HEDNO’s internal tool to assess the potential for voltage violations. In the experimental pilot setup in Mesogeia, Greece, the forecasting framework enabled the identification of undervoltage scenarios. Grid optimization algorithms were then used to determine the required flexibility, 84 kW in one case, needed to stabilize the grid. The forecasted baseline also serves as the reference point for validating the actual dispatch of flexibility.
HEDNO’s innovative use of AI for forecasting at the secondary substation level showcases the potential for DSOs to actively shape the operation of future energy systems. By integrating forecasting, grid simulation, and optimization, DSOs can proactively manage local constraints and ensure the reliability of their networks. Ongoing work will focus on enhancing model robustness and enabling real-time substitution of metered data with forecasted baselines during demand response events.
Stay tuned for more updates on HEDNO’s contribution to the HEDGE-IoT project and its pioneering efforts in flexibility and grid intelligence.
These results have been presented during the Hellenic Association for Energy Economics (HAEE) conference on 03 June, in Athens, Greece.
Authors:
- Nikolaos Fesakis,
- Theodore Tranos,
- Thomas Vasileiou,
- Maria Koutsoupidou,
- Sotirios Christopoulos,
- Georgios Loukos
Authors’ organisation:
Hellenic Electricity Distribution Network Operator (HEDNO)